Why Does My Variable Reset Every Time I Press Play in Unreal Engine 5?
A deep dive into the UE5 game loop, variable persistence, and how to manage your data effectively between sessions.
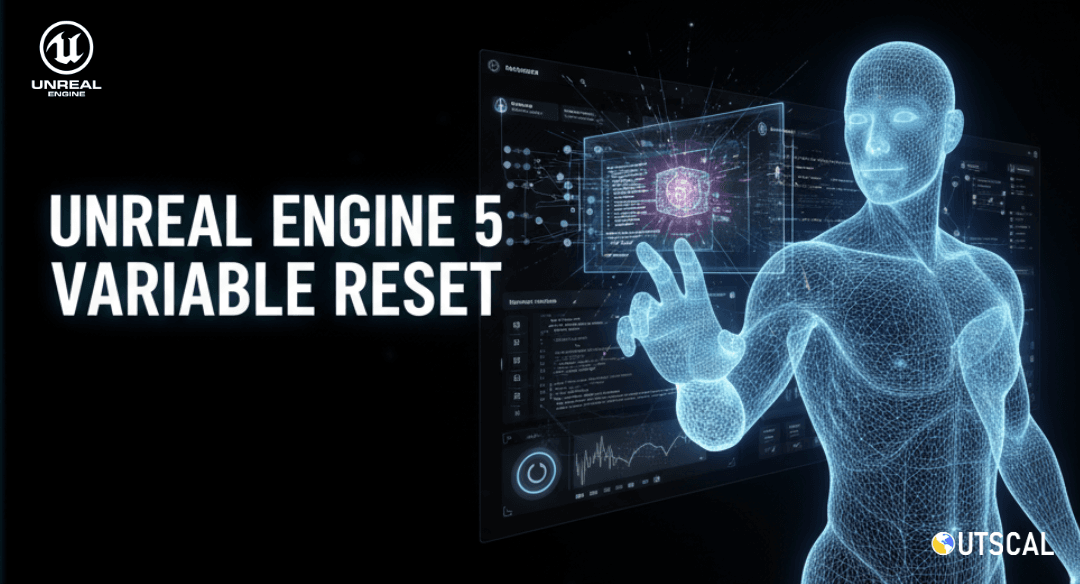
Table of Contents
Introduction
If you're new to Unreal Engine 5, you've likely encountered a common frustration: you set a variable in your Blueprint, press Play, and its value resets. This behavior can be confusing, but it's a fundamental part of how UE5 is designed to work. Understanding why this happens is the first step toward mastering variable management in your projects.
This guide will walk you through the core concepts behind UE5's variable behavior, from the distinction between Blueprints and their instances to the different ways you can manage and persist data. By the end, you'll have a clear understanding of how to control your variables and make them behave exactly as you intend.
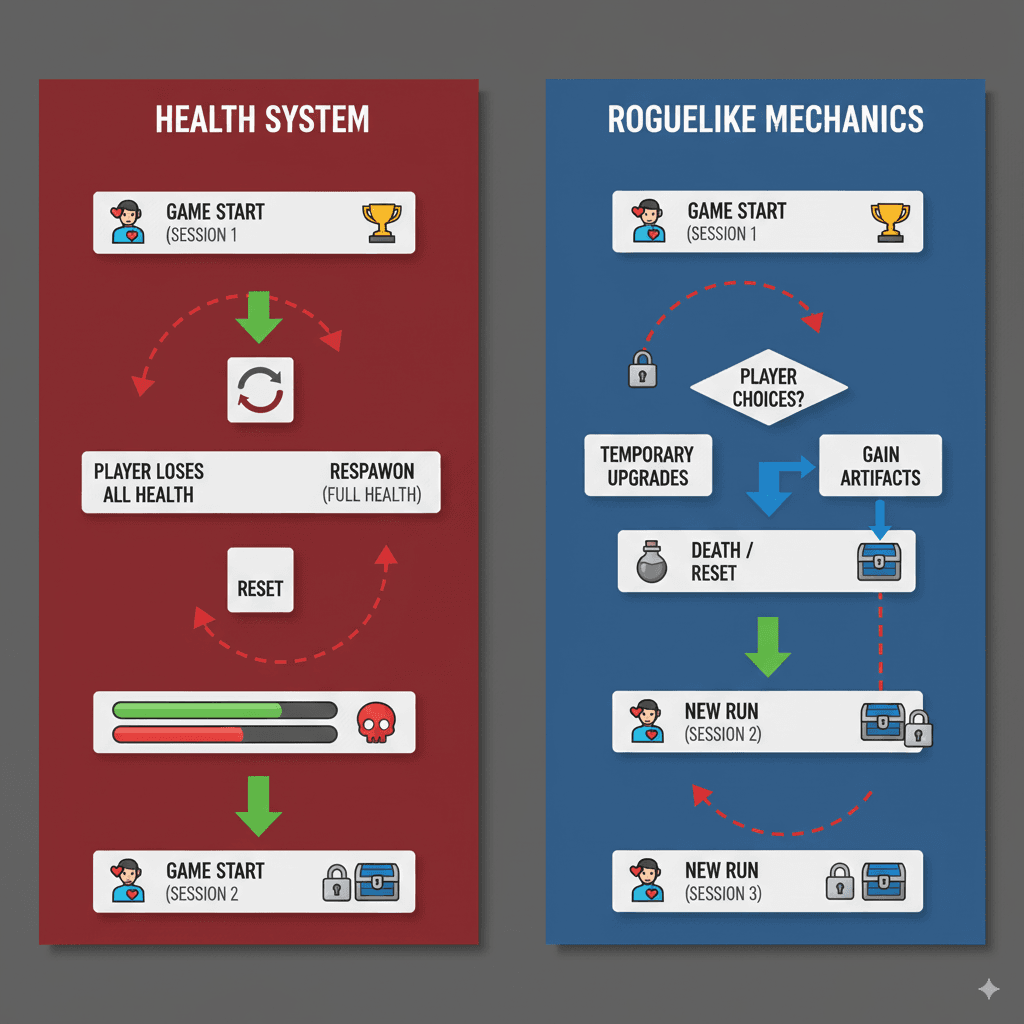
Understanding the UE5 Reset Cycle
Every time you press the Play button in the Unreal Editor, the engine kicks off a process known as "Play in Editor" (PIE). During this process, the engine creates a temporary, playable version of your game world. It takes all the Blueprints you've created and spawns instances of them in the level. These instances are essentially live copies of your Blueprints, and they are what you interact with during gameplay.
When you stop the PIE session, the engine discards this temporary world and all the instances within it. This is why any changes made to a variable during gameplay are lost—they were made to a temporary copy that no longer exists. This reset cycle is intentional and crucial for debugging, as it ensures that every play session starts from a consistent, predictable state.
Blueprint vs. Blueprint Instance: What's the Difference?
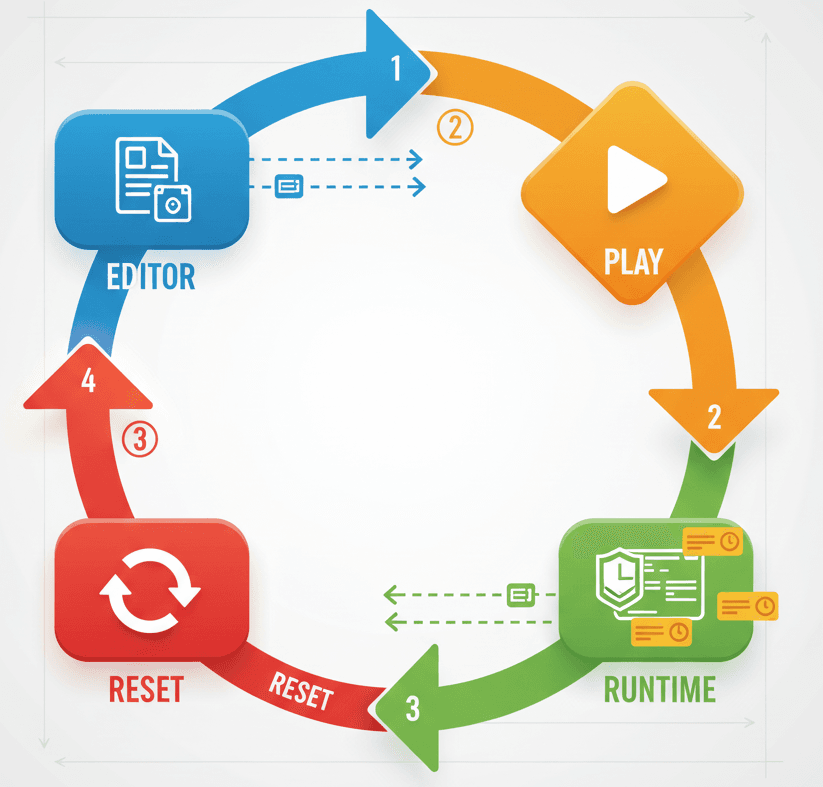
To understand variable behavior, it's essential to grasp the relationship between a Blueprint and its instance.
- Blueprint: A Blueprint is a template or a class. It defines the components, variables, and logic that an object will have. When you edit a Blueprint in the Blueprint Editor, you are defining the default state for all objects created from it.
- Blueprint Instance: An instance is a specific object in your level that has been created from a Blueprint. Each instance starts with the default values defined in its Blueprint, but these values can be changed for each specific instance.
Think of a Blueprint as a cookie cutter and instances as the cookies. The cutter defines the shape, but you can decorate each cookie differently. When you change a variable's default value in the Blueprint, it's like changing the shape of the cutter—all future cookies will have the new shape. If you change a variable on an instance in the level, you're just changing that one cookie.
Variable Management Strategies
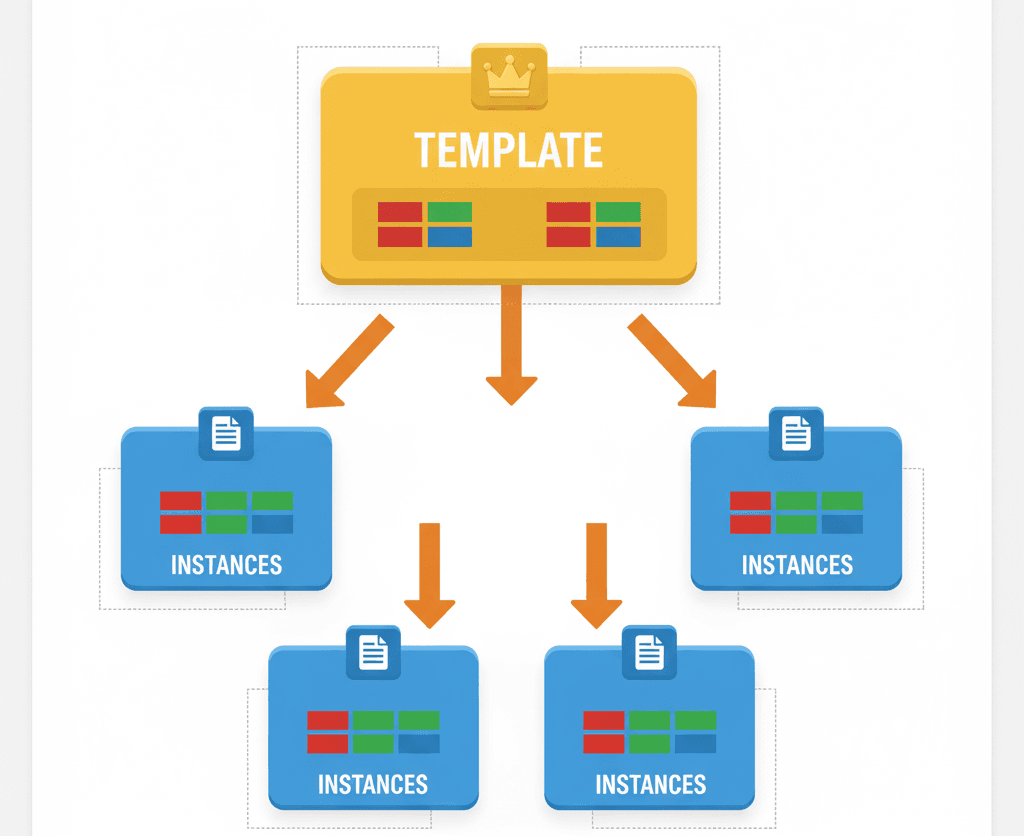
So, how do you make variable changes stick? The right approach depends on what you're trying to achieve. Here are the primary methods for managing variable data in UE5:
| Method | Description | Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| Default Value | Set in the Blueprint Editor. This is the value a variable will have at the start of every PIE session. | Defining the initial state of an object, like a character's starting health. |
| Instance Editable | A setting that allows you to change a variable's value for a specific instance in the level's Details panel. | Creating variations of an object, like setting different patrol speeds for enemy AI. |
| Game Instance | A persistent object that lasts for the entire game session. It's ideal for data that needs to survive level changes but doesn't need to be saved permanently. | Storing player scores or inventory data between levels. |
| SaveGame Object | Used for permanent data persistence. It allows you to save data to a file and load it back later. | Saving a player's progress, settings, or high scores between game sessions. |
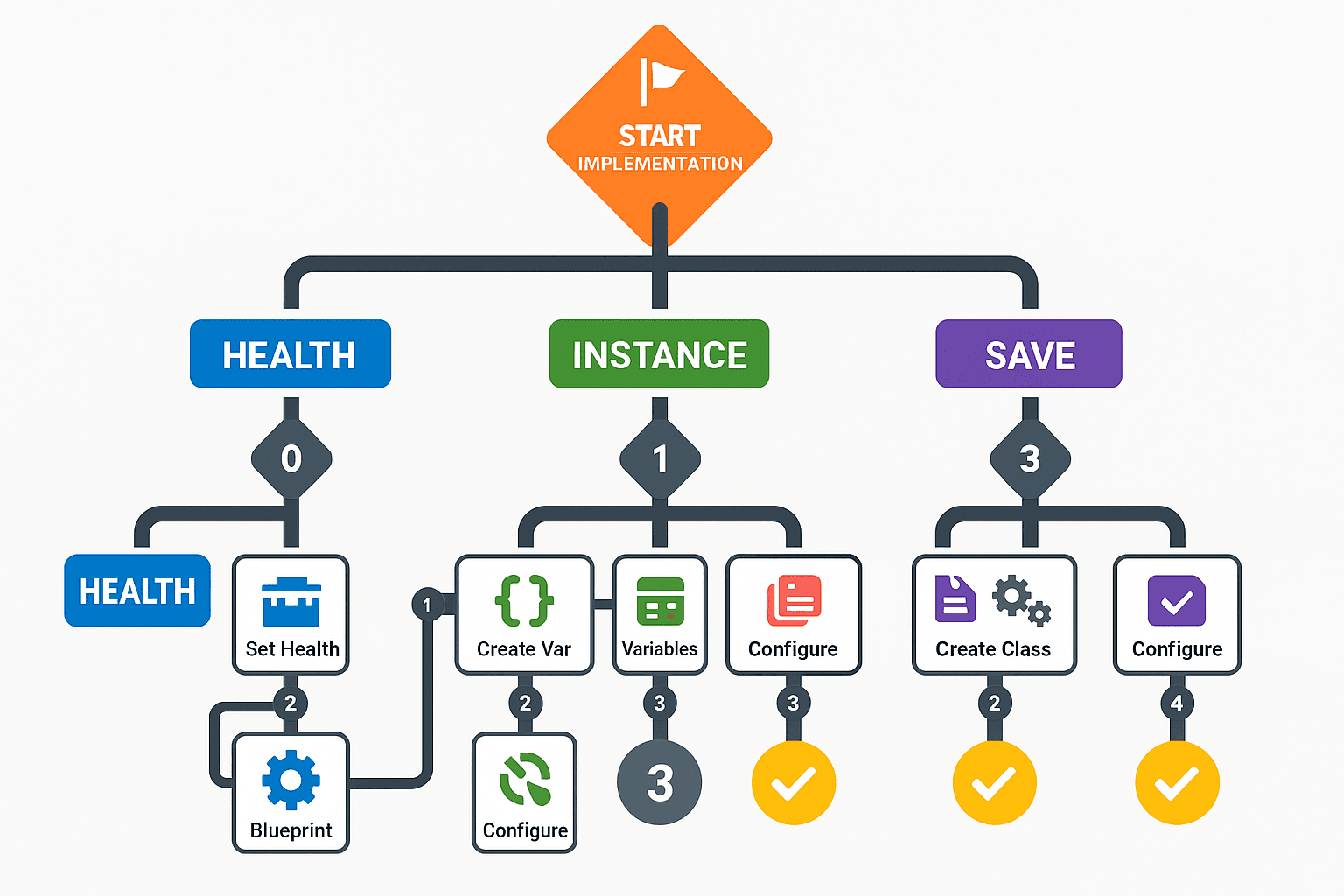
Implementation Walkthrough
Let's walk through a practical example. Imagine you have a player character with a health variable. Here's how you would manage it:
- Setting the Default: In your player character Blueprint, create a float variable named
Healthand set its default value to 100. - Making it Instance Editable: With the
Healthvariable selected, check the "Instance Editable" box in the Details panel. Now you can place multiple instances of your character in the level and give them different starting health values. - Using the Game Instance: If you want the player's health to persist between levels, you would store it in the Game Instance. When the player takes damage, you would update the variable in the Game Instance. When a new level loads, you would retrieve the health value from the Game Instance.
- Saving the Game: To save the player's health permanently, you would create a SaveGame object with a
Healthvariable. When the player saves the game, you would copy the current health to the SaveGame object and save it to a slot. When loading the game, you would do the reverse.
Game Implementation Examples
Here are a few common scenarios and the best way to handle their variables:
- Player Score: Store this in the Game Instance during gameplay so it persists across levels. When the game ends, save it to a SaveGame object to update the high score list.
- Enemy Patrol Points: These are specific to each enemy, so they should be stored in an "Instance Editable" array of vectors on the enemy Blueprint. This allows you to set up unique patrol paths for each enemy in your level.
- Collectibles: To track which collectibles have been picked up, you would need to save their status. A good approach is to give each collectible a unique ID and store a list of collected IDs in a SaveGame object.
Conclusion
The variable reset in Unreal Engine 5 is not a bug, but a feature designed to give you a clean slate for every playtest. By understanding the difference between Blueprints and instances and utilizing tools like the Game Instance and SaveGame objects, you can gain full control over your game's data. With these concepts in hand, you're well-equipped to build complex, persistent game worlds.
Key Takeaways
- Variables reset on Play because UE5 creates temporary instances of your Blueprints.
- A Blueprint is a template; an instance is a live object in the world.
- Set default values in the Blueprint Editor for the initial state.
- Use 'Instance Editable' to create variations of objects in your level.
- The Game Instance stores data that needs to persist between level changes.
- SaveGame objects are for saving data permanently between game sessions.
- Stopping a PIE session discards the temporary game world and all changes.
- Mastering these concepts is key to managing complex game states.
Common Questions
What is the difference between a Blueprint and a Blueprint Instance?
A Blueprint is a template or class that defines the properties and behaviors of an object. A Blueprint Instance is a specific object in your level created from that template. Changes made to the Blueprint affect all instances, while changes to an instance only affect that specific object.
Why do my variables reset every time I start the game?
Variables reset because each time you press Play, Unreal Engine 5 creates a new instance of your Blueprints based on their default values. This is part of the intended game loop to ensure a consistent starting state.
How can I save a variable's value between game sessions?
To save data permanently, you need to use a SaveGame object. This allows you to write variable values to a file on the player's device and load them back when the game starts.
What is the purpose of the Game Instance?
The Game Instance is a persistent object that exists for the entire duration of the game session, even when changing levels. It's ideal for storing temporary data that needs to survive level transitions but doesn't need to be saved permanently.
When should I use 'Instance Editable' for a variable?
Use 'Instance Editable' when you want to set different default values for individual instances of a Blueprint directly in the level editor. This is useful for creating variations of the same object without creating new Blueprints.
What is the UE5 Reset Cycle?
The UE5 Reset Cycle is the process where the engine discards the old game world and creates a new one every time you press Play. This ensures that each gameplay session starts from a clean, predictable state defined by the default values in your Blueprints.
How do I use a SaveGame object to store a player's score?
You would create a SaveGame Blueprint, add a variable for the score, and use the 'Save Game to Slot' node to write the data. To retrieve it, you use the 'Load Game from Slot' node.
Can I change a variable in the Blueprint and see it update in the instance immediately?
Yes, if you change a default variable value in the Blueprint Editor and compile it, all instances of that Blueprint in your level will update to reflect that new default value, unless you have manually overridden it on a specific instance.